The facilities are carefully engineered and constructed for optimal metalworking and efficiency. Read More…
At Hallman Foundry, we specialize in the production of high-quality grey iron castings, bringing precision, consistency, and strength to each component we create. With decades of experience in foundry operations, we understand the unique properties of grey iron and harness our expertise to deliver castings that are both durable and meticulously crafted.

For over a century Lemfco has been a family business and leading manufacturer of high-quality grey iron castings. We pride ourselves on our extensive list of products and patterns available for our customers. Lemfco is committed to creating the best gray iron castings for our customers to fit all of their needs. Our company has changed throughout the years, but our commitment to quality never has.
Our gray iron castings are second to none. These high performance items are pre-tested for maximum customer satisfaction. We have a component staff that can easily handle your requests. Turn to Interstate Castings for the best gray iron castings. You will not be upset with the quality of items you receive. We look forward to working with your business. Give us a call today!

At Hiler Industries, we present ourselves as dedicated manufacturers of grey iron castings engineered to deliver strength, consistency, and long-term reliability for demanding industrial applications. We work with carefully controlled melt processes, high-quality raw materials, and disciplined foundry practices to produce castings that maintain uniform microstructure, predictable mechanical...

At St. Marys Foundry, Inc., we take immense pride in our longstanding tradition of crafting exceptional grey iron castings. With years of experience under our collective belt, we are renowned for our commitment to quality and precision in the production of these castings. Our products are a testament to our dedication to excellence. We specialize in the creation of grey iron castings that serve a ...

More Iron Foundry Companies
To successfully accomplish the iron casting process, modern foundries utilize advanced equipment and specialized supplies designed to analyze and blend raw materials prior to subjecting them to extremely high temperatures. This meticulous preparation is essential for transforming solid metal into molten iron, which can then be shaped into a wide variety of industrial and commercial products. Once liquefied, the cast iron is poured into custom-designed molds. These molds may be manufactured on-site at the foundry or produced by external mold suppliers, depending on the facility’s capabilities and the specifications of the particular casting project.
Understanding the Iron Casting Process: Step-by-Step Overview
The iron casting process is central to the manufacturing of durable components for numerous industries. The process begins with the careful selection and testing of raw materials, including pig iron, scrap steel, and various alloying elements. Foundries often utilize advanced spectroscopic analysis to ensure chemical composition meets strict quality standards required for different applications such as automotive, construction, and heavy machinery.
Once the material blend is confirmed, it is melted in a furnace—commonly a cupola furnace or an induction furnace—capable of reaching the high temperatures necessary to liquefy iron and its alloys. The use of cupola furnaces allows for continuous operation and precise temperature control, which is critical in producing consistent, high-quality cast iron. During this stage, impurities are removed, and alloying elements are added to impart specific mechanical properties such as tensile strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance.
Key Questions for Foundry Buyers
- What are the most important factors to consider when selecting an iron foundry for your project?
- How do foundries maintain quality and consistency in their casting operations?
- Which types of cast iron (e.g., grey iron, ductile iron, white iron) best suit your application?
- What are the typical lead times for custom iron castings?
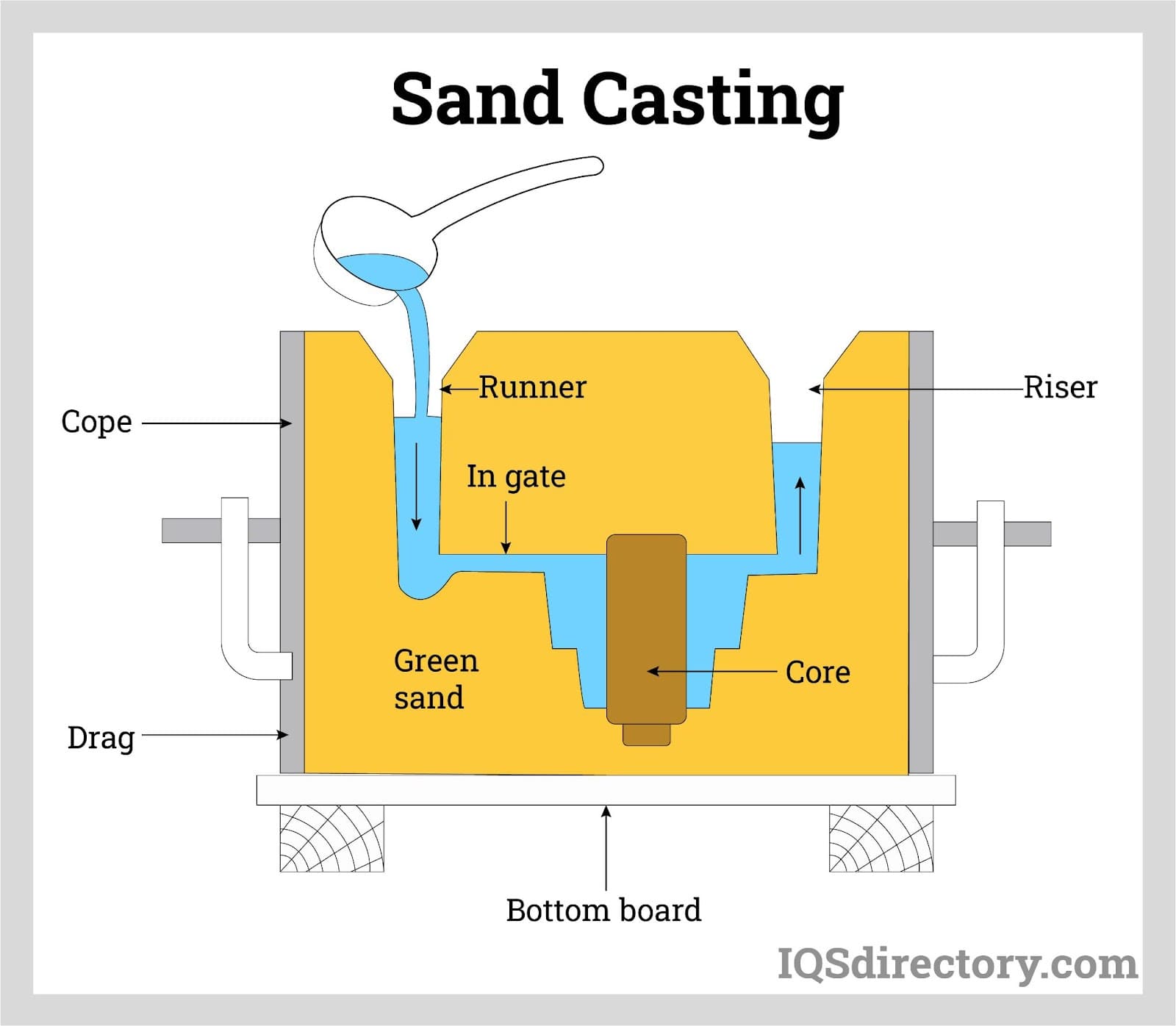
The next step involves pouring the molten cast iron into robust molds. Mold design is a critical factor in the casting process and can significantly affect the final product’s performance. Molds may be manufactured using sand casting, shell molding, or investment casting techniques, each offering distinct advantages for different production volumes and part geometries. Whether the molds are created within the foundry or sourced from specialized mold manufacturers, precision in mold making is vital for achieving tight tolerances and intricate shapes.
Cooling, Finishing, and Post-Processing in Iron Foundries
After filling, the mold—along with its molten contents—must be carefully cooled to solidify the part. Cooling methods vary depending on the complexity and size of the cast component. While some iron foundries allow the casts to cool at ambient room temperature, others employ advanced, controlled cooling technologies to manage the cooling rate. Controlled cooling is essential for influencing the internal microstructure and final mechanical properties of the casting, such as hardness and resistance to wear.
Cooling systems may include water spray chambers, forced air tunnels, or even specialized cooling beds. The choice of cooling method has a direct impact on production efficiency, casting integrity, and the ability to meet tight delivery schedules. Foundries must also allocate significant floor and storage space to accommodate cooling equipment, finished castings, and pre-production materials. Efficient layout and logistics are critical to optimizing workflow and minimizing production bottlenecks.
Industries and Applications Benefiting from Iron Castings
Iron foundries serve a wide variety of industries thanks to the versatility and durability of cast iron products. Some of the most common application sectors include:
- Automotive Manufacturing: Engine blocks, brake drums, manifolds, and suspension components.
- Agriculture: Tractor parts, plowshares, irrigation system components, and combine frames.
- Water and Sewage Treatment: Pipe fittings, valves, pump housings, and grates.
- Construction and Building: Structural supports, manhole covers, architectural features, and reinforcement brackets.
- Machinery and Equipment: Gearboxes, housings, machine tool beds, and hydraulic system parts.
- Transportation: Train wheels, couplers, railcar components, and heavy vehicle parts.
- Electronics: Enclosures and cooling plates for electrical equipment.
Specialization vs. Versatility in Modern Iron Foundries
While some foundries process a broad range of ferrous and non-ferrous metals, many facilities benefit from developing a specialty in iron casting. Specialization allows foundries to stay competitive in the rapidly evolving field of metallurgy by offering in-depth expertise, process optimization, and tailored customer support. Specialized iron foundries are often equipped to produce high-volume runs of grey iron castings, ductile iron components, or custom alloy products for demanding customers.
Conversely, versatile foundries capable of pouring multiple metals—such as steel, bronze, and aluminum—can provide a one-stop solution for clients with diverse casting needs. When choosing a foundry partner, decision-makers should consider not only the materials offered but also the facility’s technical capabilities, quality certifications, and track record of delivering complex projects on time and within budget.
How to Evaluate Iron Foundries for Your Project
When sourcing iron casting services, it’s important to assess several key decision factors:
- Material Capabilities: Can the foundry produce the specific grade of cast iron or alloy required?
- Production Capacity: What are the minimum and maximum order quantities? Does the foundry support prototyping or low-volume runs?
- Quality Assurance: Does the foundry have ISO certifications, documented inspection processes, and in-house testing facilities?
- Lead Time and Logistics: What are typical production timelines, and does the foundry offer shipping or just-in-time delivery options?
- Secondary and Value-Added Services: Are machining, surface finishing, heat treating, and assembly available?
- Industry Experience: Has the foundry worked with similar clients or produced comparable parts?
Asking these questions during your research can help you identify a reliable partner and streamline your project from concept through completion.
Types of Molds and Casting Techniques in Iron Foundries
Iron castings can be produced using a variety of mold types and casting techniques, each suited to specific part geometries, production volumes, and quality requirements:
- Solid Pattern Molds: Used for simple shapes, these single-piece molds are cost-effective for small production runs.
- Split Pattern Molds: Composed of two halves—a cope (top) and a drag (bottom)—this method allows for more intricate geometries and easier removal of finished castings.
- Core Processes: Incorporating cores enables the creation of internal cavities or complex shapes, essential for producing engine blocks, pumps, and valve bodies.
- Gravity Pouring: Relies on gravity to fill the mold, suitable for most iron casting applications.
- Vacuum and Pressure Pouring: Used for high-precision or thin-walled castings, these methods ensure complete mold filling and reduce the risk of air entrapment.
Each technique offers unique benefits in terms of cost, precision, and suitability for different use cases. Selecting the right casting method is critical to achieving the required mechanical properties and surface finish for your application.
Controlling Microstructure and Mechanical Properties
Careful control of the cooling process is vital for shaping the microstructure of cast iron parts. The cooling rate influences the formation of graphite flakes (in grey iron), nodules (in ductile iron), or cementite (in white iron), each imparting unique mechanical characteristics. Foundries may use controlled cooling to:
- Enhance tensile strength
- Improve wear and abrasion resistance
- Achieve desired hardness or ductility
- Prevent internal defects such as porosity or cracking
After cooling, castings are removed (ejected) from the molds. At this stage, most cast iron parts display surface irregularities such as burrs, flash, or rough edges. To ensure the finished product meets precise specifications, foundries perform a range of surface finishing processes including grinding, sanding, shot blasting, and precision machining. These operations are essential for preparing castings for further assembly or direct end use.
What Finishing Options Are Available for Iron Castings?
- Grinding and Sanding: Removes excess material and smooths surfaces.
- Machining: Achieves tight tolerances and precise dimensions.
- Shot Blasting: Cleans surfaces and improves fatigue life.
- Painting and Coating: Adds corrosion protection and enhances appearance.
Secondary Operations and Value-Added Services in Iron Foundries
Many iron foundries offer a wide range of secondary operations and value-added services designed to streamline the supply chain and reduce the need for external vendors. These services include:
- Painting and Powder Coating: Provides corrosion resistance and aesthetic customization.
- Galvanizing: Adds a protective zinc layer for use in harsh or outdoor environments.
- Heat Treating: Alters the mechanical properties of the casting to meet demanding application requirements.
- Assembly: Enables delivery of subassemblies or finished products, reducing lead times and simplifying logistics for customers.
Decision-makers should evaluate the full range of services available at a given foundry to ensure alignment with their production needs, quality expectations, and long-term cost efficiencies.
Iron Foundry Facility Considerations
The layout, equipment, and operational practices of a foundry play a significant role in its ability to deliver high-quality castings cost-effectively. Key facility considerations include:
- Floor and Storage Space: Sufficient area for staging raw materials, finished goods, molds, and cooling equipment.
- Modern Melting Technology: Use of energy-efficient cupola or induction furnaces for lower operating costs and environmental compliance.
- Advanced Mold Handling Systems: Automation and robotics for increased throughput and worker safety.
- Environmental Controls: Emissions reduction, dust collection, and heat recovery systems.
Facilities that invest in continuous improvement, lean manufacturing, and green foundry initiatives are better positioned to meet the evolving demands of global markets.
Ready to Source Custom Iron Castings?
Are you looking for a reliable iron foundry to manufacture custom cast iron parts for your next project? Learn more about cast iron products and services or request a quote today. Whether you need high-volume production, rapid prototyping, or value-added services, the right foundry partner can help you achieve your goals with quality, efficiency, and competitive pricing.
Frequently Asked Questions About Iron Casting and Foundries
- What types of cast iron are available? Common varieties include grey iron, ductile iron, white iron, and malleable iron, each with distinct mechanical properties suitable for specific applications.
- How do I choose between sand casting, shell molding, and investment casting? The choice depends on part complexity, volume, required tolerances, and cost considerations. Sand casting is most common for large parts and medium runs, while shell and investment casting excel at high-precision, intricate components.
- What are typical turnaround times for custom iron castings? Lead times vary by foundry, project complexity, and order size, but can range from a few weeks for standard parts to several months for highly customized orders.
- Can iron foundries provide design and engineering support? Many modern foundries offer design-for-manufacturing (DFM) assistance, CAD modeling, and prototype testing to help optimize component design before production.
- Are iron castings cost-effective for small production runs? While tooling costs can be a factor, many foundries offer flexible solutions for low- and mid-volume orders, including rapid prototyping and short-run production services.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Iron Foundry for Your Needs
Iron casting remains one of the most reliable and versatile manufacturing processes for producing durable metal parts across a wide range of industries. Modern foundries combine traditional expertise with cutting-edge technology to offer customers cost-effective, high-quality solutions tailored to specific performance requirements. When selecting an iron foundry, consider factors such as material specialization, production capabilities, quality assurance, and available value-added services. By partnering with a skilled foundry, you can ensure reliable supply, consistent part quality, and long-term success for your business.
Ready to take the next step? Explore our full range of cast iron solutions or contact us today to discuss your project requirements and receive a customized quote.







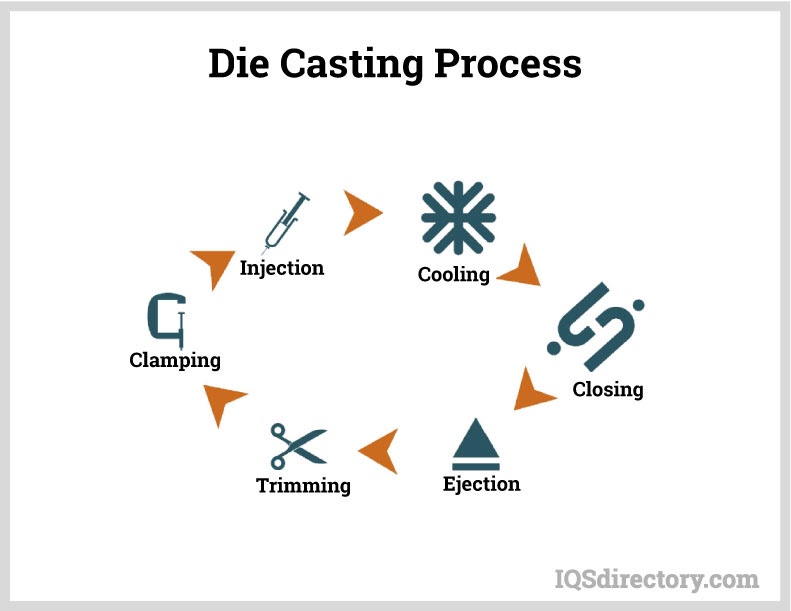
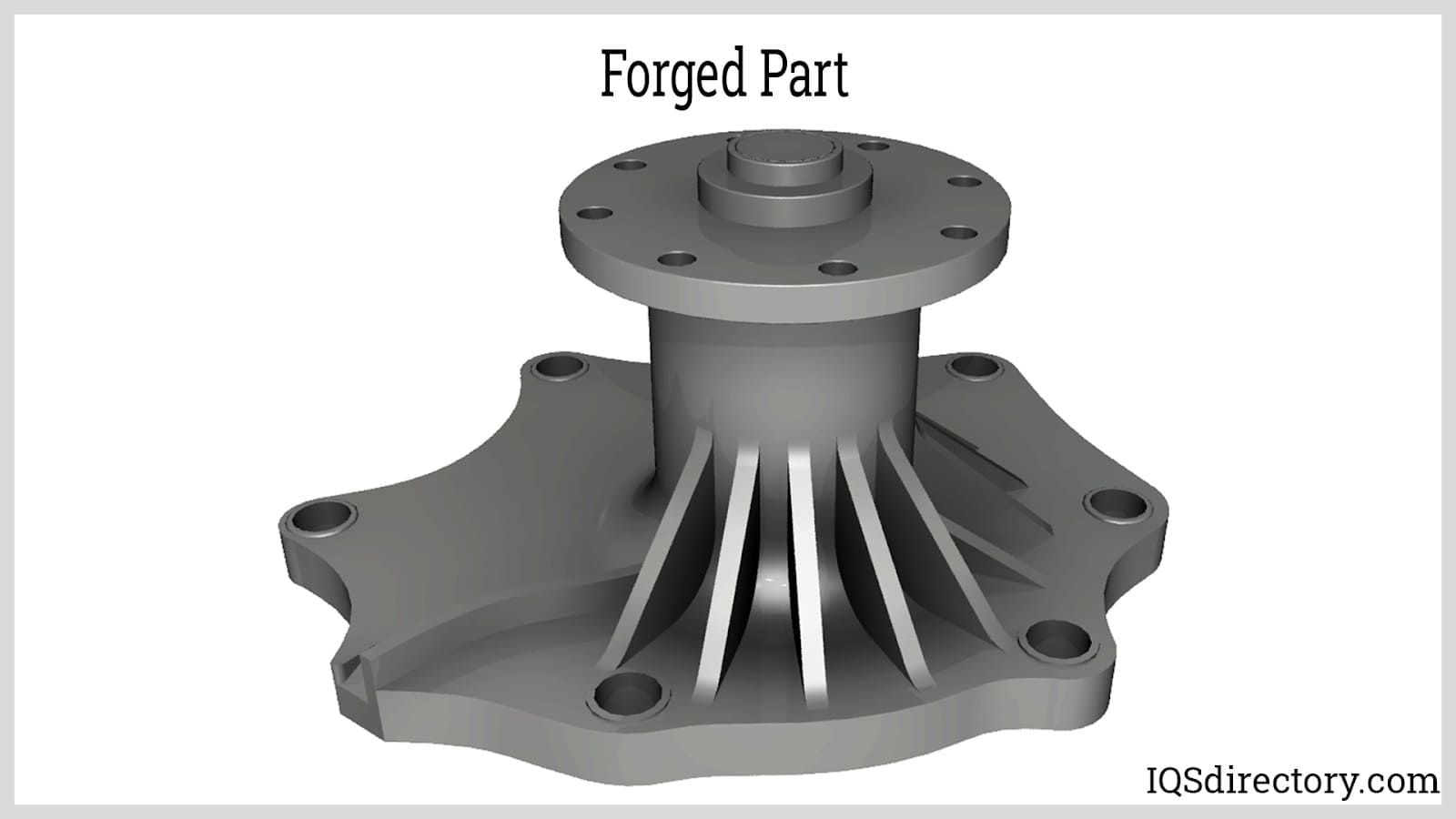
 Die Castings
Die Castings Forgings
Forgings Grey Iron Castings
Grey Iron Castings Investment Castings
Investment Castings Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services